Appeals Court Tosses Out Death Sentence For Boston Marathon Bomber
BY DAVID WELNA
A death penalty sentence against confessed Boston Marathon bomber Dzhokhar Tsarnaev was thrown out Friday by a federal appeals court in Boston.
Citing errors by a lower court, a three-judge panel from the 1st U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals sent the widely publicized case back to the federal District Court that had convicted Tsarnaev in 2015 and ordered six death sentences for him as well as 11 concurrent life sentences.
In the ruling, that court was ordered to impanel a new jury and hold a sentencing retrial for the death penalty convictions.
“A core promise of our criminal-justice system is that even the very worst among us deserves to be fairly tried and lawfully punished,” Judge O. Rogeriee Thompson wrote in the 224-page opinion, noting the District Court judge had failed to vet the trial’s jurors adequately for bias.
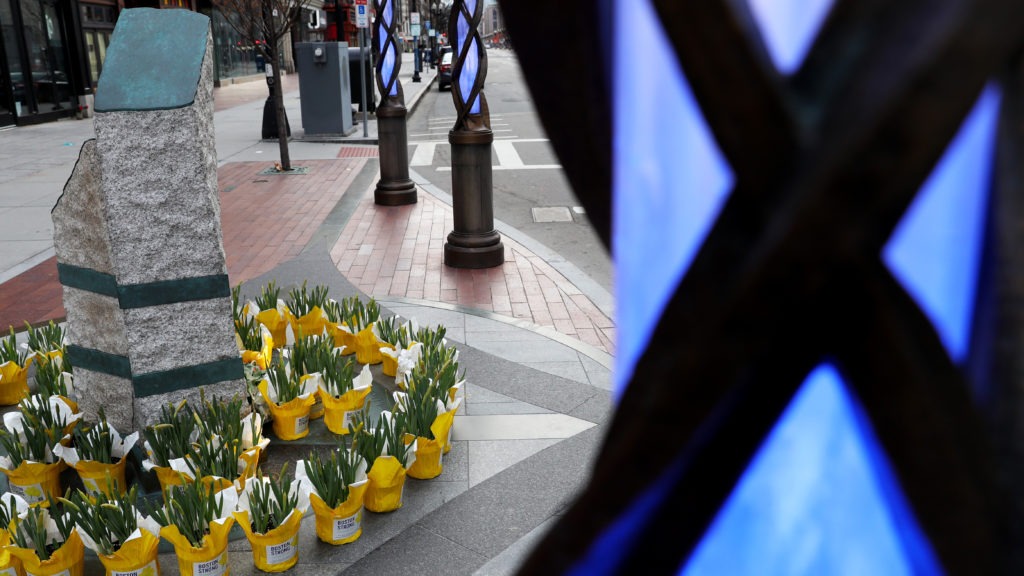

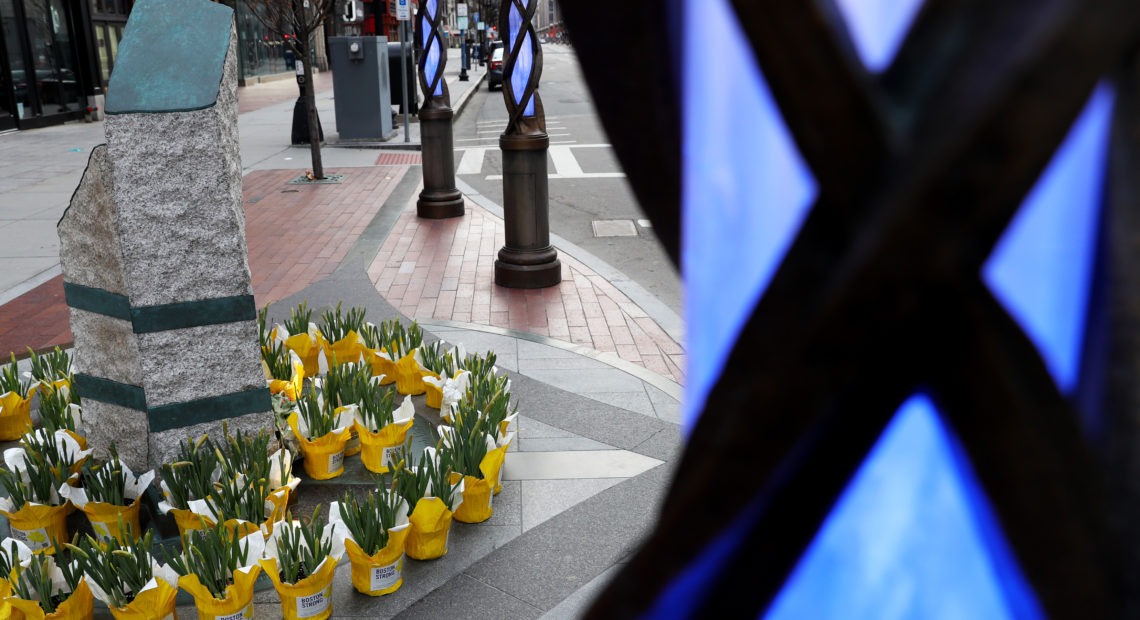
Flowers are placed at the memorial to the victims of the 2013 Boston Marathon bombings on April 20.
CREDIT: Maddie Meyer/Getty Images
Attorneys for Tsarnaev have acknowledged that he and his older brother Tamerlan, who was killed during the manhunt that followed the 2013 bombing, detonated two homemade pressure cooker bombs that killed three people and wounded at least 260 others near the finish line of the annual foot race.
“I am sorry for the lives I have taken, for the suffering that I have caused you, for the damage I have done, irreparable damage,” Tsarnaev told the courtroom on the day he was sentenced, adding “in case there is any doubt, I am guilty of this attack, along with my brother.”
Tsarnaev, who is now 27, is being held at the high-security supermax federal prison near Florence, Colo.
While the appellate court vacated the death sentences against the younger of the Tsarnaev brothers, it also made clear that he would never again be a free man.
“Dzhokhar will remain confined to prison for the rest of his life,” Thompson wrote, “with the only question remaining being whether the government will end his life by executing him.”
The higher court noted that the judge who presided over Tsarnaev’s trial had rejected the defense team’s request for a more distant trial venue where prospective jurors might be less likely to be prejudiced against the Chechen immigrant. That judge did so, the ruling maintained, promising that local jurors would be adequately screened.
But the three-judge panel ruled that the trial judge had failed to impanel an impartial jury.
“The judge stopped Dzhokhar’s counsel from asking prospective jurors questions like ‘[w]hat did you know about the facts of this case before you came to court today (if anything)?’ ” Thompson wrote, “and ‘[w]hat stands out in your mind from everything you have heard, read[,] or seen about the Boston Marathon bombing and the events that followed it?’ ”
In another part of the opinion, Judge Juan Torruella wrote that the District Court judge relied on “self-declarations of impartiality” by prospective jurors, calling that “an error of law and an abuse of discretion.”
“Tsarnaev presented a colorable claim that Juror 286 knowingly withheld from the court the fact that she posted twenty-two online comments mourning the death of [8-year-old bystander] Martin Richard,” Torruella wrote of the woman who would become the jury’s foreperson, “praising law enforcement officers (three of whom would later testify at trial), expressing ‘BOSTON STRONG’ civic pride, and calling Tsarnaev a ‘piece of garbage.’ ”
Torruella also noted that three of the 12 jurors who voted admitted before the trial that they were convinced Tsarnaev was guilty, while another two said they believed he took part in the bomb attack.
“With a jury so intensely impacted by the charged crimes,” the appellate judge continued, “and so exposed to inflammatory pretrial publicity — including reports detailing the extreme anguish of their neighbors and repeated calls for Tsarnaev to be sentenced to death — I cannot say with any degree of certainty that the jurors did not possess a ‘predilection toward that penalty.’ ”
“In sum,” Torruella concluded, “the government cannot show that the jury that convicted Tsarnaev and recommended that he be put to death was impartial.”
9(MDAyOTk4OTc0MDEyNzcxNDIzMTZjM2E3Zg004))