ICE Removes Immigration Detainees From Federal Prisons, Including Washington; 3 Remain In Oregon
READ ON
U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement has all but abandoned its use of federal prisons to house detainees.
In early June, the agency announced it was sending up to 1,600 immigrant detainees to five federal prisons in Texas, Oregon, California, Washington, and Arizona.
But now, a total of only three ICE detainees remain across the five prisons that once held hundreds of immigrants. Immigrant detainees left the federal prisons either because they were deported, transferred to civil detention facilities, or were granted bail
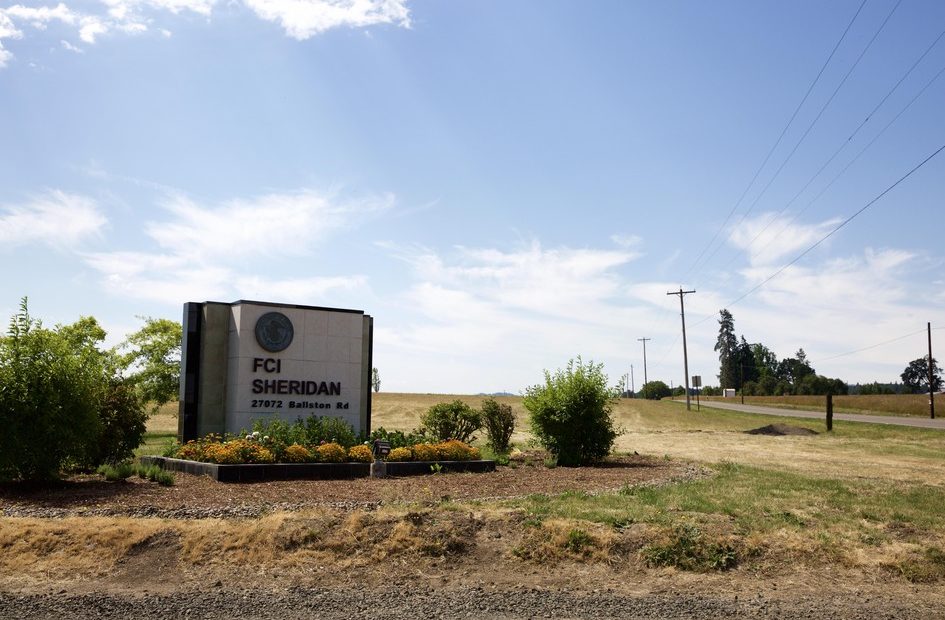
There are no ICE detainees at the federal prisons in Victorville, Calif., SeaTac in Washington state, La Tuna in Texas, or Phoenix, ICE spokeswoman Tanya Roman said in a statement Wednesday. The three ICE detainees that remain are inside the federal prison in Sheridan, Ore.
ICE’s large-scale use of federal prisons to house its detainees was unprecedented and controversial. Many of the detainees sent to the prisons were seeking asylum. Yet, they were treated as criminals, according to multiple immigration attorneys who represented the detainees in several of the prisons, even though few — if any — of the detainees had been charged criminally or were serving a criminal sentence.
“ICE was blending the criminal, penal corrections system, blending it with the immigration, asylum system and sort of creating this unified view that they all need to be detained and incarcerated,” says Stephen Manning, a Portland-based immigration attorney. He represents the three remaining ICE detainees at the federal prison in Oregon.
Manning’s firm, the Portland-based Innovation Law Lab, originally represented more than 80 individuals held at the prison. The government moved their asylum cases forward because all of Manning’s clients were found to have valid asylum claims.
“It was an abject failure of government policy to use the federal prisons for the detention of asylum seekers and I hope this constitutionally risky experiment, which failed, resonates and that we won’t see it again,” Manning says..
ICE didn’t say if the dramatic reduction in detainees being held in federal prisons represented a change in policy.
“The interagency agreements with BOP [Bureau of Prisons] were set up as a temporary measure to meet the increased need for detention space during the implementation of the U.S. Department of Justice’s zero-tolerance policy,” says Roman, the ICE spokeswoman. “Detainees that were held there would either have been removed, released from custody or transferred to another facility.”
ICE’s agreements to use federal prisons are valid until June 2019, meaning the agency could put detainees back in federal prisons.
But Corene Kendrick, a staff attorney at the nonprofit Prison Law Office in Berkeley, Calif. doesn’t think that will happen, at least not in southern California. She worked with the ACLU to file a lawsuit that would keep detainees out of the federal prison in Victorville.
“The removal of the immigration detainees shows that there are limits to the Trump administration’s zero tolerance policy towards asylum seekers and immigrants,” says Kendrick. “By just putting people in a medium security prison, which is designed for convicted prisoners, the Department of Homeland Security and BOP were violating the constitutional rights of the immigrants and asylum seekers.”
Immigration detainees are held in civil detention, which under the law is supposed to be a higher standard than criminal detention.
But that’s not always the case.
Jorge Baron, executive director of the Northwest Immigrant Rights Project, says some asylum seekers being held in the federal prison near Seattle told him the treatment in the federal prison was better than the civil detentions’ facilities where they had been housed in the past.
“This is not to say I saw it as a positive that they were in this prison, but just that how bad our immigration detention system is that folks who end up in a federal prison feel like that’s a more human treatment, which gives me serious pause,” he says.
The fact that, for now, ICE has dramatically reduced its used of federal prisons does little to ease Baron, who says ICE is continuing its efforts to detain people.
“Now they’re ramping up more facilities down on the southern border,” he says. “So they may not be using the federal prisons, but they’re still detaining an incredibly high number of people throughout the country.”
Related Stories:

Immigration enforcement concerns cause mixed attendance trends in North Central WA schools
Eastmont Junior High School students make their way past the 800 wing on the way to their second period in East Wenatchee. (Credit: Jacob Ford / Wenatchee World) Listen (Runtime

These churches offer shelter and sanctuary to vulnerable migrants. Here’s why
Bishop Joseph Tyson (left) and the Rev. Jesús Mariscal (right) of the Yakima Diocese worry about how their parishioners will cope with broad changes to immigration policy, which have had

Lawsuits draw attention to role of local authorities in enforcing federal immigration policy
Two lawsuits against the Adams County Sheriff’s Office have drawn attention to the role of state and local authorities in enforcing federal immigration laws.