Researchers In Seattle Show Polluted Stormwater Hurts Fish Survival
Each time it rained during an eight-week period in the winter of 2015, someone from Jenifer McIntyre’s team drove up to Seattle and collected stormwater near the Highway 520 bridge across Lake Washington.
It was a rainy stretch, so that meant 25 trips.
After each trip, McIntyre says, “we would bring the dirty runoff to the fish” — the larval fish the team was rearing in Indianola on the eastern side of Puget Sound — “and expose them to that for 24 or 48 hours.”
The researchers were trying to figure out whether or not stormwater affects fish even before they hatch. And they learned that it does: When fish grow up in stormwater instead of clean water, they go out into the world less equipped to survive. The study, published this week in Scientific Reports, a Nature research journal, found that fish reared in stormwater emerged from their eggs with fewer of the hair-like sensors they rely on to sense predators and prey.
That was true even for zebrafish, a tropical freshwater fish used in scientific research, which normally survives in stormwater.
Since fish that can’t sense predators or prey are likely to have a tough go of it, McIntyre says the upshot is “what doesn’t kill you can still kill you, in fact.”

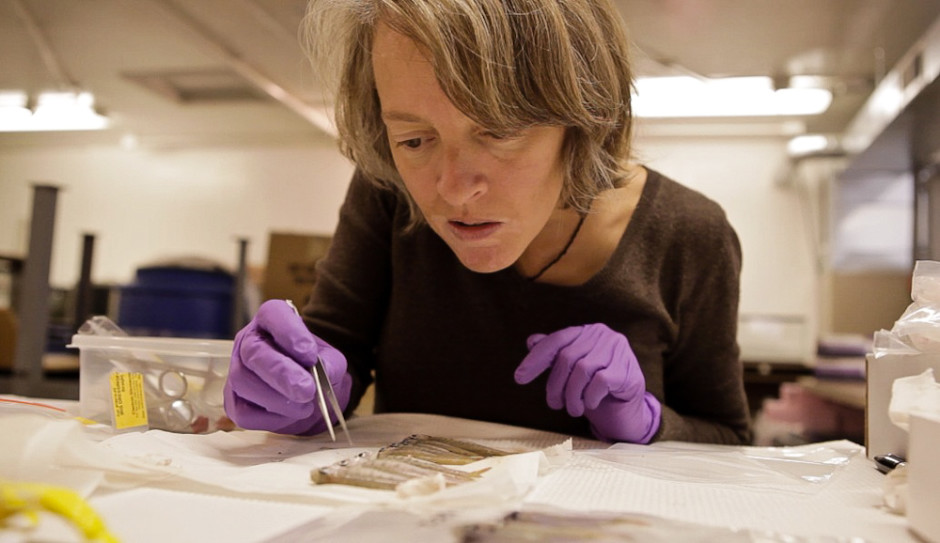
WSU professor Jenifer McIntyre and NOAA research toxicologist Julann Spromberg are pictured in this 2012 file photo studying the effectiveness of rain gardens by filtering runoff through these soil columns. CREDIT: KATIE CAMPBELL/KCTS9/EARTHFIX
Normally, rain gardens can help protect fish from toxic runoff. That’s because soil and plants can pick up a lot of pollutants and toxins from storm-water and keep them out of streams and lakes.
Coho salmon, for example, die in unfiltered stormwater but can live in stormwater filtered through a rain garden. The researchers were surprised to learn that, in this case, rain gardens didn’t seem to help. Fish reared in rain garden-filtered storm water still ended up with compromised sensory systems.
McIntyre says that means it’s crucial to figure out which of the many toxins in stormwater is to blame so the pollutant can be eliminated at its source.
Copyright 2018 Earthfix
Related Stories:

Head Start serves 15,000 kids in Washington. And its regional office just closed.
The regional Head Start office closed this week, making some advocates nervous about the program’s future. (Credit: Barnaby Wasson / Flickr Creative Commons) Listen (Runtime 1:00) Read The regional Head
Washington, Idaho rank high for public health emergency preparedness
Both states saw steady or increased funding for public health, but Idaho still among lowest for vaccinations.

How does climate affect your life? Tri-Cities survey open now
Cities, towns and counties are starting to plan for a future with climate change. Now, the Tri-Cities area is asking people about regional hazards and historical trends. (Credit: Simon Foot












