Oregon Sues Monsanto For PCB Clean-Up Costs
Oregon is suing the agro-chemical company Monsanto to help clean up toxic chemicals in the environment. The Attorney General’s Office filed suit Thursday in Multnomah County Circuit Court.
The suit is seeking at least $100 million to cover decades of cleanup of a now-banned group of chemicals called PCBs, or polychlorinated biphenyls, which the company manufactured.
The state alleges Monsanto knew of the toxic effects of the PCBs in its products, yet continued to sell them. Now, Oregon Attorney General Ellen Rosenblum says the company needs to pay.
“We’ve spent millions of dollars cleaning up PCBs and we have legal standing to sue to recover the cost. So basically, we’ve spent the money. You guys caused the damage. We want you to pay for it,” she said.
PCBs were widely used in flame retardants, paint and electrical insulation until being banned in 1979. The chemicals are toxic to wildlife and humans, and are extremely slow to break down in the environment. They continue to contaminate waterways across the state, including the Columbia and Willamette Rivers and Coos Bay.
Kevin Parrett of the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality says the state has been laboriously cleaning up PCB pollution for three decades. It’s often a mechanical process that requires the removal or capping of contaminated sediment.
“We’ve estimated that DEQ has spent $100 million that has been unrecovered. So obviously that’s been a major impact on DEQ’s budget,” he said.
And those costs are expected to continue to amass as clean-up efforts continue at different sites throughout the state – including at the Portland Harbor Superfund site (should that state be held responsible for part of the clean-up costs) and at “orphan” sites (contaminated private property where the responsible party is absent or unable to pay for clean-up).
“Through this action, the State seeks to recover damages from Monsanto for the costs that the State has incurred, and will continue to incur, to remediate the widespread damage caused by the presence of Monsanto’s PCBs on Oregon’s lands, in Oregon’s waters, and throughout Oregon’s natural environment,” states the complaint.
In an email statement, Monsanto calls the Oregon lawsuit “baseless” and says the suit is counterproductive to clean-up efforts already underway.
The Port of Portland, the cities of Portland, Seattle and Spokane, as well as the state of Washington are among the governments nationwide to have already sued the company.
But Rosenblum says Oregon is taking a different legal tact she believes will be easier to support in court.
“One of the reasons that we felt strongly that we should bring this lawsuit is that we’re kind of looking at it through different lens in terms of the claims and the bases,” she said.
These include claims of public nuisance and trespass. The complaint also says Oregon intends to add to the suit, “demanding compensation for the value of the fish, wildlife, and fish and wildlife habitat injured or destroyed and the cost of restoring wildlife production.”
Related Stories:
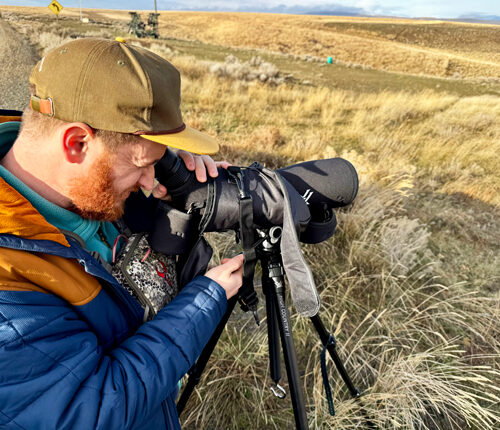

Searching for sage grouse: Looking for a chicken-sized needle in south-central WA
Seth Hulett, Audubon Washington’s senior program manager of the Columbia Plateau, searches through his spotting scope for sage grouse. (Credit: Courtney Flatt / NWPB) Listen (Runtime 4:12) Read In south-central

Landfill neighbors worry about PFAs contamination seeping into drinking water
A view of the landfill from Carole Degrave’s property line. (Credit: Courtney Flatt / NWPB) Listen (Runtime 0:54) Read For years, some people who live near a Central Washington landfill
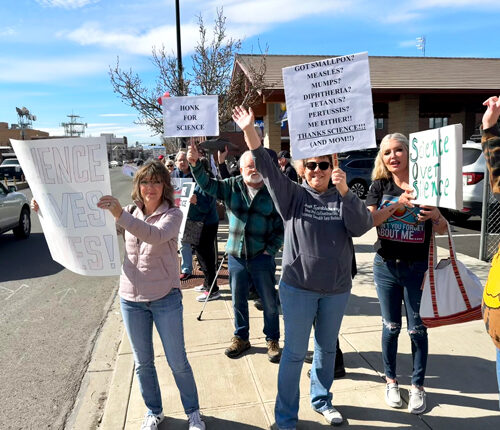

Dozens in Yakima rally to support science for national protest
Around 50 people gathered for Yakima’s Stand Up for Science rally on Friday. People around the country attended science protests at the same time. (Credit: Courtney Flatt / NWPB) Listen